Although not as commonly used as lead-acid or lithium-ion batteries, nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries remain a preferred option for specific electronic applications requiring rechargeable power. These batteries are composed of nickel oxide hydroxide, metallic cadmium electrodes, and an alkaline electrolyte solution (potassium hydroxide). Their versatility has made them popular in devices such as power tools, portable electronics, and emergency backup systems.
NiCd battery pack offer several notable advantages that have led to their continued use.
NiCd batteries are capable of storing a significant amount of energy within a compact size. This high energy density makes them ideal for applications where space and weight are limited.
One of the standout features of NiCd batteries is their ability to endure numerous charge-discharge cycles. This longevity makes them suitable for devices requiring long-term power, reducing the frequency of replacements.
NiCd batteries perform reliably across a wide range of temperatures, including extreme cold and heat. This durability enhances their versatility, allowing them to operate effectively in various environments without sacrificing performance.
NiCd batteries can be charged quickly, minimizing downtime. This rapid charging feature is beneficial in situations where fast power restoration is necessary.
NiCd batteries maintain consistent and reliable performance over their lifespan, with stable voltage output during most of the discharge cycle. This makes them a trusted choice for applications where uninterrupted power is critical.
While NiCd batteries offer several benefits, they also have notable drawbacks.
One significant limitation of NiCd batteries is the memory effect. This occurs when the battery’s capacity is reduced if it is not fully discharged before being recharged. Over time, this can lead to a decline in performance if not managed correctly. While proper charging practices can help mitigate the memory effect, it remains a concern for applications that demand peak battery performance.
Although NiCd battery pack use an alkaline electrolyte solution, which is less harmful than the acidic solutions found in other conventional batteries, they present significant environmental challenges due to cadmium. This toxic heavy metal, used in the electrodes, poses serious risks to both health and the environment. To minimize its impact, proper disposal and recycling are essential. As environmental awareness increases, the use of cadmium in batteries has come under scrutiny, sparking efforts to find more eco-friendly alternatives.
NiCd batteries generally have a lower energy density compared to newer technologies like lithium-ion. This results in shorter operating times and reduced efficiency in applications where energy conservation is critical. Although NiCd batteries are known for their reliability and durability, their limited energy density makes them less suitable for applications requiring extended runtime, leading many manufacturers to opt for alternatives like lithium-ion or nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries.
NiCd batteries have a relatively high self-discharge rate, meaning they lose charge even when not in use. This can reduce performance if the battery is left unused for an extended period. Although periodic maintenance charging can help mitigate this issue, it remains a consideration for users who need to store batteries for long durations without degradation.
Another drawback of NiCd battery pack is their relatively heavy and bulky design compared to some alternative battery technologies. This can pose challenges in applications where space and weight are important factors. Despite this, NiCd batteries continue to be a popular choice in areas where their reliability and other advantages outweigh concerns about size and weight.
Nickel-cadmium batteries are known for their high energy density, long cycle life, wide operating temperature range, fast charging capability, and reliable performance. However, they also have several disadvantages, including the memory effect, environmental concerns due to cadmium, lower energy density compared to newer technologies, a relatively high self-discharge rate, and bulky design. The suitability of NiCd batteries depends on the specific requirements of each application, and users must carefully weigh their advantages against these limitations.
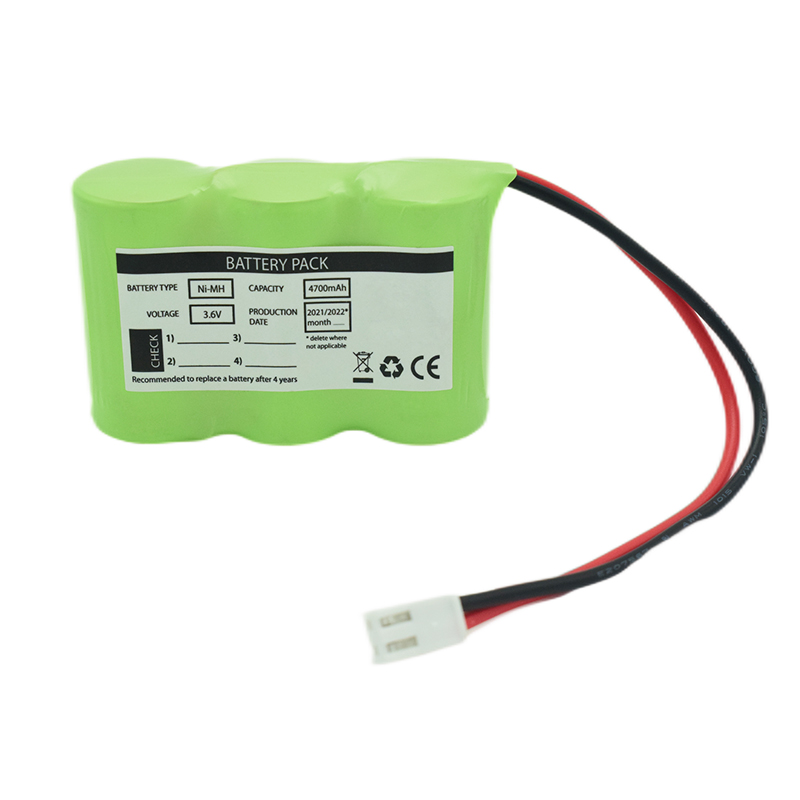
 Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V
Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V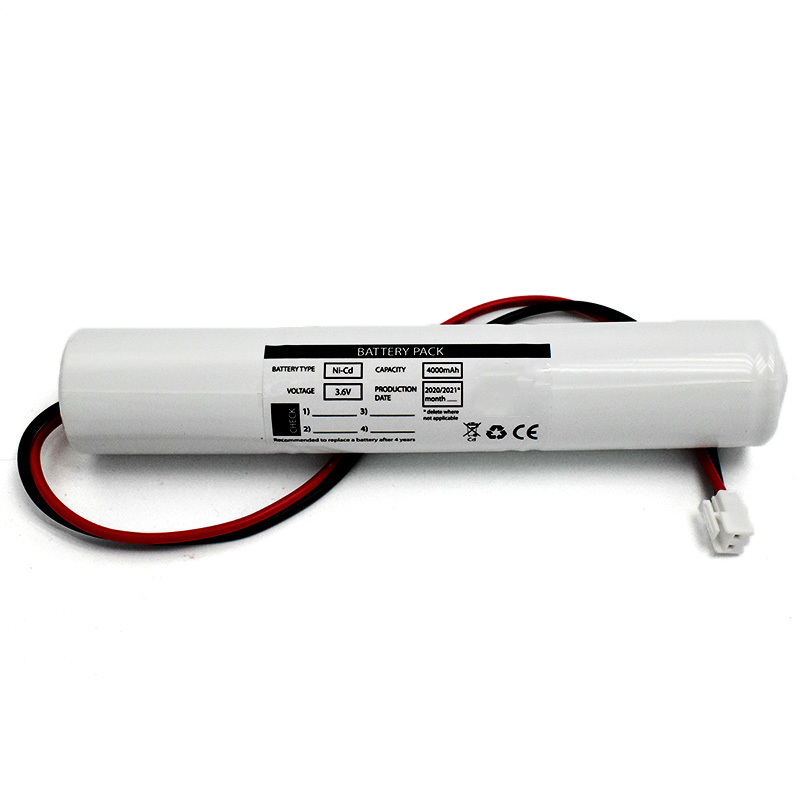 Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V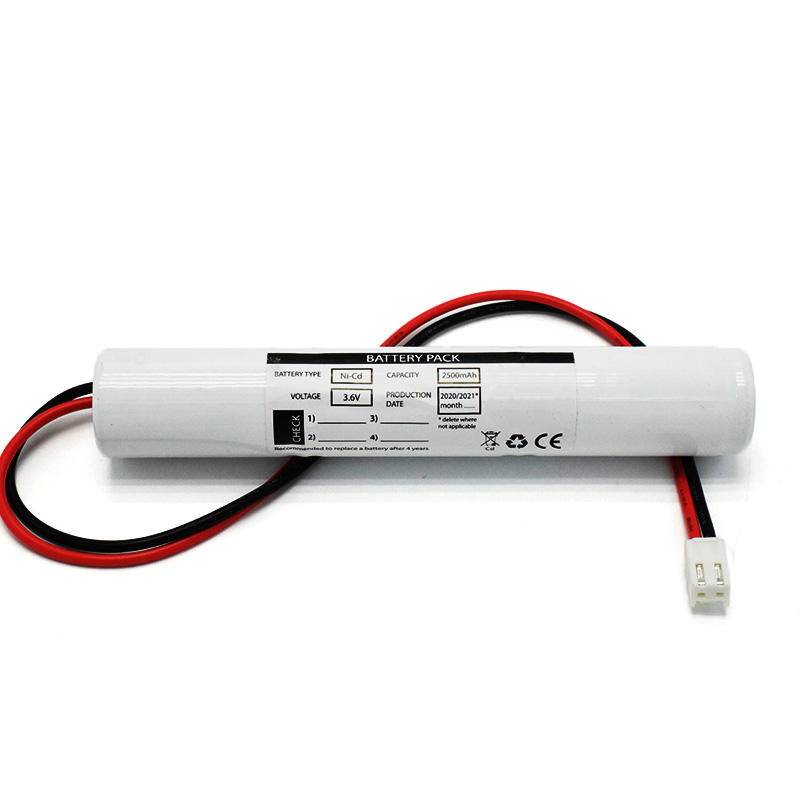 Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V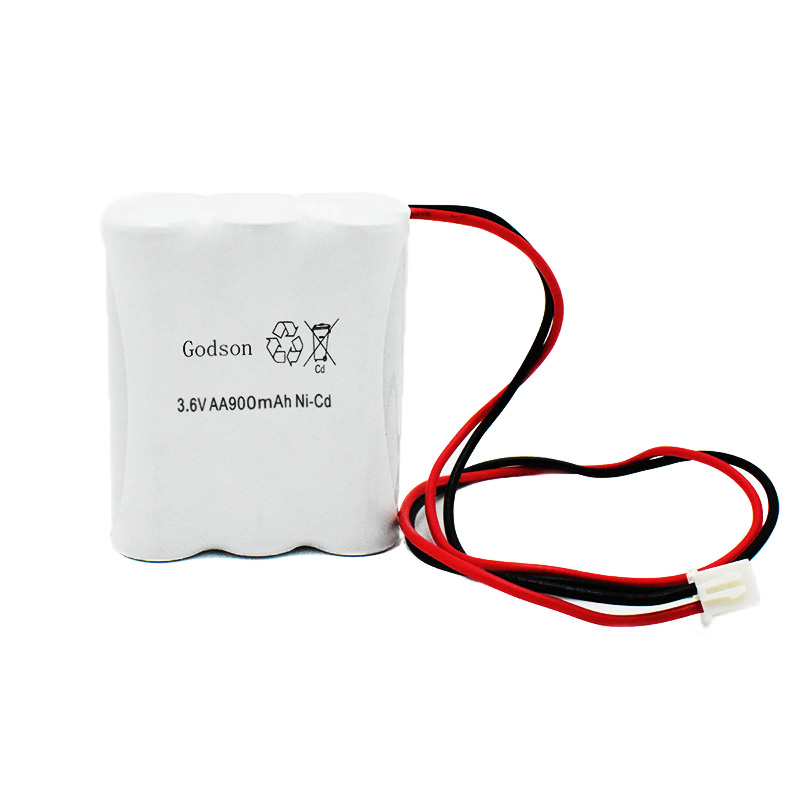 NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V
NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V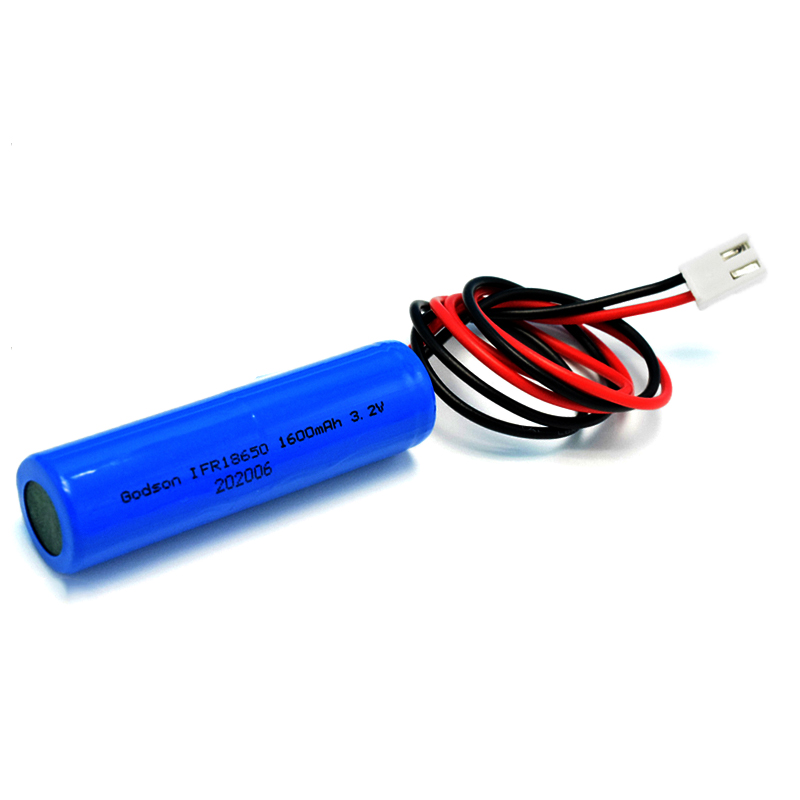 LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V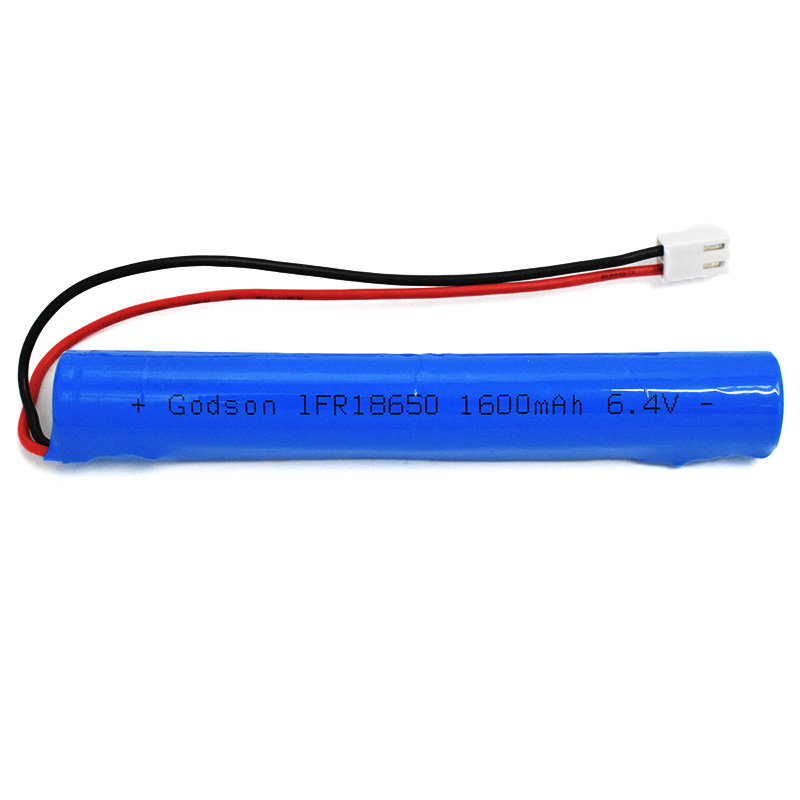 LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V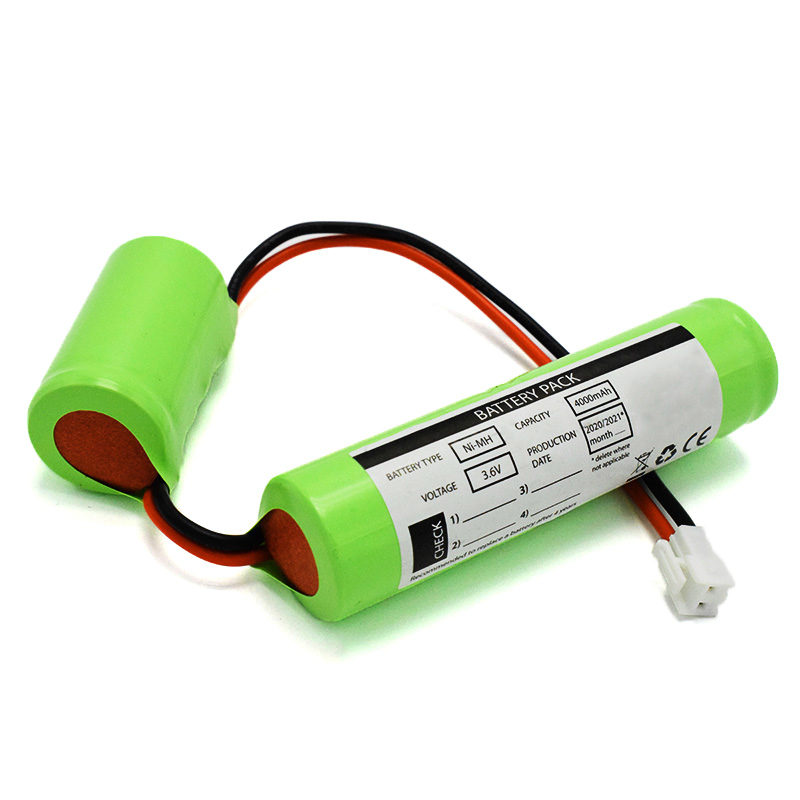 Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V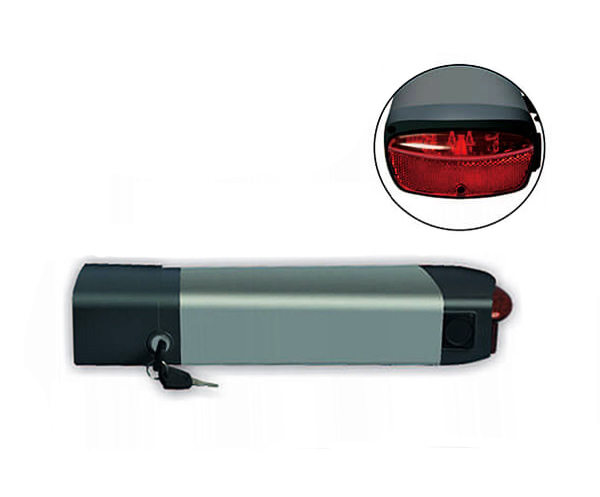 E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1
E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1 E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian
E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian