Nickel-Metal Hydride batteries have become a crucial component in various modern applications. These batteries are known for their reliability, environmentally friendly nature, and ability to power everything from consumer electronics to hybrid vehicles. But what makes Ni-MH batteries so special? Let's dive into their principles, types, structure, and applications.
Ni-MH batteries are a type of rechargeable battery that uses a nickel oxide hydroxide (NiOOH) cathode and a hydrogen-absorbing alloy anode. This type of battery was developed as an improvement over Nickel-Cadmium (Ni-Cd) batteries, offering higher energy density and reduced environmental impact.
Nickel–metal hydride batteries store more energy than nickel–cadmium batteries. The negative electrode, which is a metal hydride mixture, consists of the potassium hydroxide electrolyte and the positive electrode, the active material of which is nickel hydroxide.
The chemical composition of Ni-MH batteries allows them to store and release energy efficiently. During charging, the nickel hydroxide in the cathode is oxidized, and hydrogen ions are absorbed by the metal hydride anode. When discharging, this process is reversed, releasing stored energy.
There are two main types of Ni-MH batteries:
1. Standard Ni-MH Batteries: These are the most common type and are used in a wide range of applications.
2. Low Self-Discharge (LSD) Ni-MH Batteries: These batteries retain their charge for longer periods, making them ideal for devices that are not used frequently.
The structure of Ni-MH batteries includes an anode, cathode, and electrolyte. The anode is typically made from a hydrogen-absorbing alloy, while the cathode is made from nickel oxide hydroxide. The electrolyte is usually a potassium hydroxide solution, which facilitates the flow of ions between the anode and cathode.
- The casing provides crucial functions such as sealing, waterproofing, and explosion prevention. It is usually made of metal or plastic and encloses the internal components, including the positive and negative electrodes, electrolytes, and separators.
The chemical reaction at the positive electrode is similar to that of the nickel-cadmium cell (NiCd), with both using nickel oxide hydroxide (NiOOH).
- The negative electrode uses a hydrogen-absorbing alloy as its primary active material. During charging, this material absorbs hydrogen ions, reducing them to form hydrogen gas while releasing electrons and producing electrical current.
- The electrolyte is vital for enabling ion and electron transport, facilitating electrochemical reactions, and maintaining overall battery performance. In Ni-MH batteries, a potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution is commonly used as the electrolyte.
- The separator is a barrier that physically separates the positive and negative electrodes, preventing direct contact, which could lead to short circuits, and ensuring the proper functioning of the electrolyte.
- High Energy Density: They can store more energy than Ni-Cd batteries, making them suitable for high-drain applications.
- Environmentally Friendly: Unlike Ni-Cd batteries, Ni-MH batteries do not contain toxic cadmium, making them a greener option.
Despite their benefits, Ni-MH batteries have some limitations:
- Cost: Ni-MH batteries can be more expensive compared to other battery types, and generate heat at extreme temperatures. These factors should be considered when choosing a battery technology for specific applications.
- Lower Voltage: Ni-MH batteries have a lower nominal voltage (1.2V) compared to other battery types like Lithium-ion (Li-ion).
- Emergency lighting battery
- Emergency lighting products
- E-bike battery and
- F-power tool battery
When comparing Ni-MH batteries with other technologies:
- Ni-MH vs. Ni-Cd: Ni-MH batteries have a higher energy density and are more environmentally friendly than Ni-Cd batteries.
- Ni-MH vs. Li-ion: While Li-ion batteries offer higher energy density and voltage, Ni-MH batteries are more cost-effective and safer in some applications.
Nickel-Metal Hydride batteries offer a unique combination of performance, cost-effectiveness, and environmental friendliness. From powering everyday electronics to enabling hybrid vehicles, these batteries are indispensable in today’s technology-driven world. If you're looking for reliable energy storage solutions, consider Ni-MH batteries as your go-to option. And if you need more information or assistance, don't hesitate to contact us; we're here to help as your trusted supplier.
1. What is the lifespan of Ni-MH batteries?
Ni-MH batteries typically last between 500 to 1000 charge cycles, depending on usage and care.
2. How do Ni-MH batteries compare to Lithium-ion batteries?
Ni-MH batteries are more affordable and safer but have lower energy density and voltage compared to Lithium-ion batteries.
3. Can Ni-MH batteries be recycled?
Yes, Ni-MH batteries are recyclable, and many recycling programs are available for proper disposal.
4. What are the best uses for Ni-MH batteries?
Ni-MH batteries are ideal for consumer electronics, hybrid vehicles, and power tools.
5. How to choose a Ni-MH battery supplier?
Look for a supplier with a good reputation, quality products, and excellent customer support to ensure you get the best Ni-MH batteries.
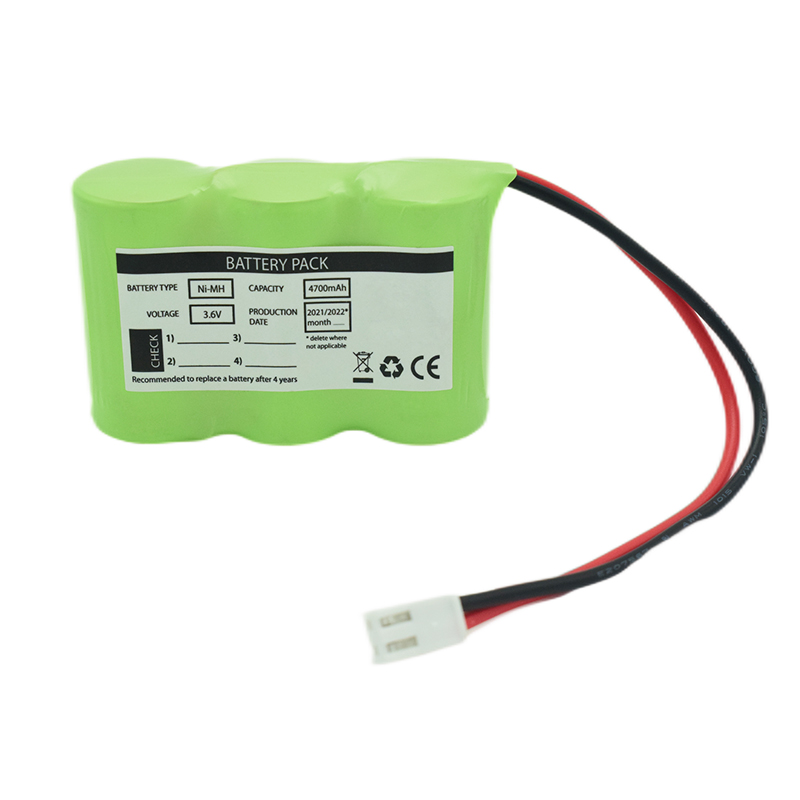
 Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V
Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V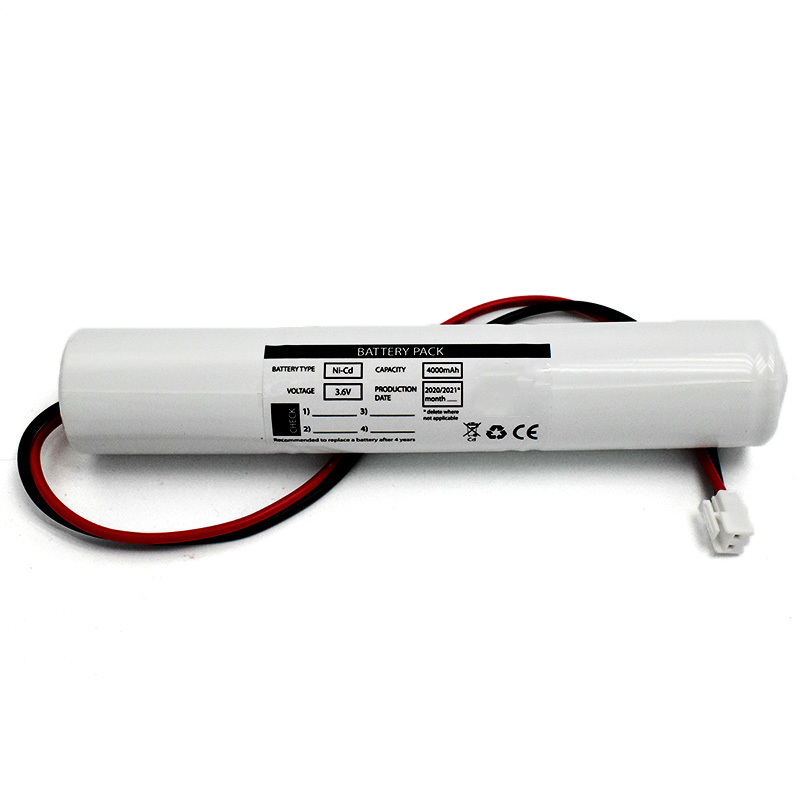 Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V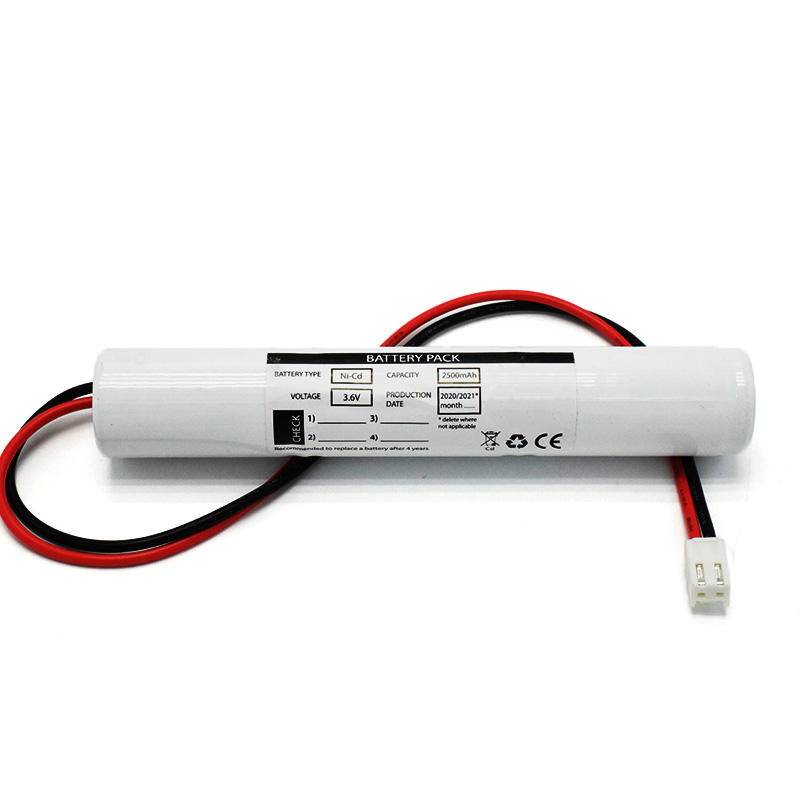 Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V
NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1
E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1 E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian
E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian