Batteries are the lifeblood of modern technology, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. Among the plethora of battery chemistries available, two contenders have stood the test of time: Nickel Cadmium (NiCd) and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4). Both offer unique advantages and disadvantages, catering to different applications and requirements. In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of NiCd and LiFePO4 batteries, comparing their characteristics, performance, and suitability for various use cases.
NiCd batteries consist of electrodes made from nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium, with an alkaline electrolyte solution. This chemistry has been widely used for decades due to its robustness and reliability. However, concerns over cadmium's toxicity and environmental impact have led to stricter regulations and a gradual decline in NiCd's popularity.
LiFePO4 batteries, on the other hand, utilize lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material, along with a lithium-based electrolyte. This chemistry offers several advantages over traditional lithium-ion batteries, including enhanced safety, thermal stability, and a longer cycle life. LiFePO4 batteries have gained traction in applications where safety and longevity are paramount, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems.
LiFePO4 batteries have almost twice the energy density than Ni-Cd batteries. This is one of the largest most favorable characteristics of LiFePO4 batteries as compared to Ni-Cd batteries. NiCd batteries typically exhibit lower energy density compared to LiFePO4 batteries. This means that NiCd batteries store less energy per unit volume or weight, resulting in bulkier and heavier battery packs for a given capacity. In contrast, LiFePO4 batteries offer higher energy density, enabling more compact and lightweight designs, which is advantageous in portable electronics and electric vehicles.
One of the standout features of LiFePO4 batteries is their exceptional cycle life. These batteries can endure thousands of charge-discharge cycles with minimal capacity degradation, making them ideal for long-term use in demanding applications. NiCd batteries also offer respectable cycle life but generally fall short of LiFePO4 batteries in this regard, especially at higher discharge rates and extreme operating conditions.
Safety is a paramount concern in battery design, particularly in applications where the risk of thermal runaway or fire is elevated. LiFePO4 batteries have a proven track record of superior safety performance, thanks to their inherent thermal stability and reduced susceptibility to dendrite formation, which can lead to short circuits and internal failures. NiCd batteries, while relatively robust, pose a greater risk of thermal runaway and are subject to stricter transportation and handling regulations due to the presence of cadmium.
Despite their declining popularity, NiCd batteries still find niche applications where their unique properties are advantageous. These include emergency lighting systems, backup power supplies, and aviation electronics, where reliability, wide operating temperature range, and resistance to overcharging are paramount.
LiFePO4 batteries have found widespread adoption in a diverse range of applications, including electric vehicles, solar energy storage systems, and portable electronics. Their combination of high energy density, long cycle life, and safety make them well-suited for environments where performance and reliability are critical, such as automotive propulsion and off-grid power generation.
In the dynamic landscape of battery technology, the choice between Nickel Cadmium (NiCd) and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) depends on a multitude of factors, including performance requirements, safety considerations, and environmental concerns. While NiCd batteries offer robustness and reliability in certain applications, LiFePO4 batteries stand out for their superior energy density, cycle life, and safety profile.
Ultimately, the decision comes down to matching the battery chemistry with the specific needs of the application, weighing factors such as energy density, cycle life, safety, and environmental impact. By carefully evaluating these parameters, engineers and designers can select the optimal battery solution to power their innovations and propel technological progress forward.
For inquiries about NiCd or LiFePO4 batteries, or to find a reliable battery supplier for your project, please don't hesitate to contact us.
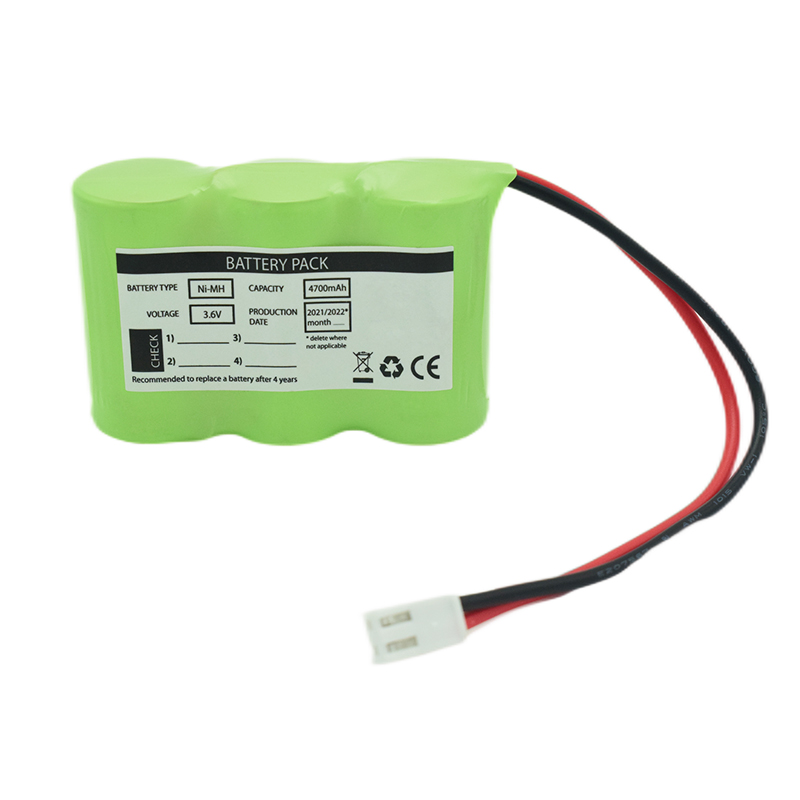
 Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V
Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V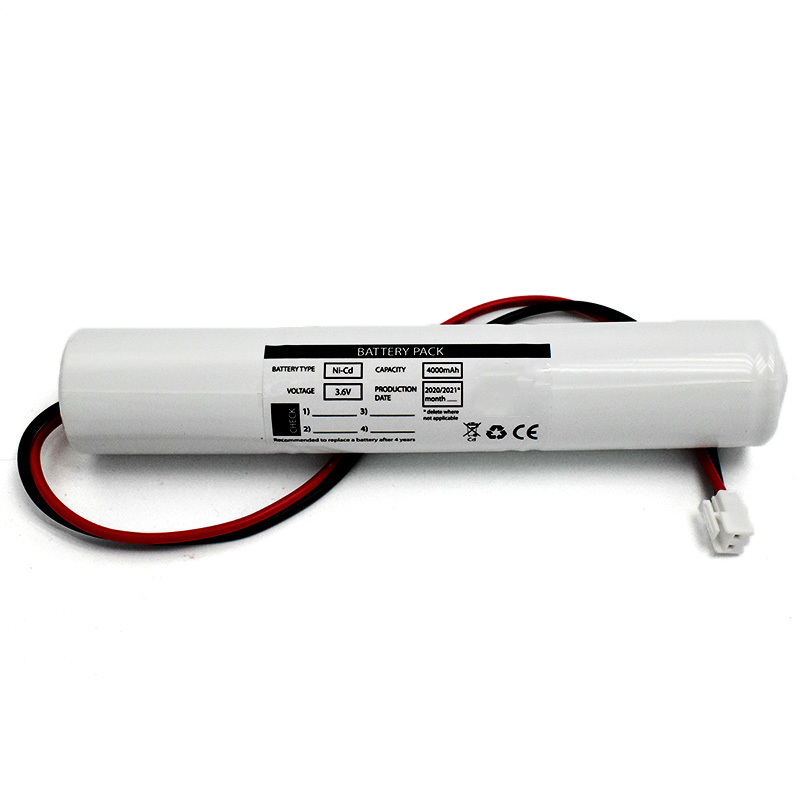 Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V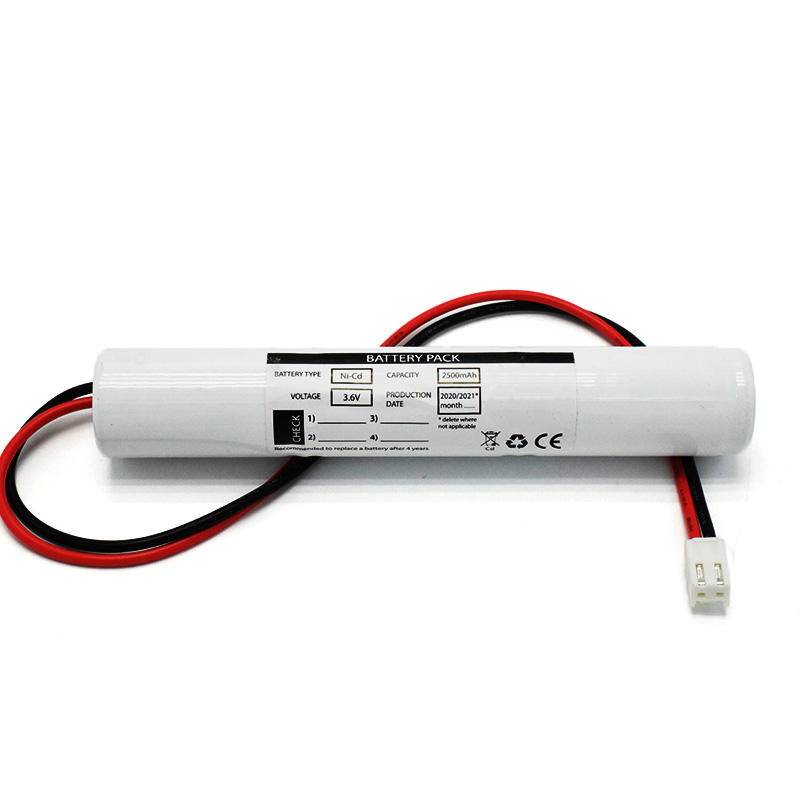 Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V
NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1
E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1 E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian
E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian