The Lithium-ion Battery is a rechargeable battery that relies on the movement of lithium ions between positive and negative poles to complete the charging and discharging work. When the battery is charged, the lithium ions generated on the anode are moved to the negative electrode through the electrolyte, and the more lithium ions are embedded into the negative carbon layer, the higher the battery capacity is. Similarly, when the battery is discharged, the lithium ions in the negative carbon layer move to the positive pole, and the more lithium ions in the anode, the higher the discharge capacity.
Commonly called Lithium Batteries are commonly used as lithium ion batteries, such as mobile phones and notebook computers. Lithium batteries are easily confused with lithium-ion batteries. It main difference is that they are using different materials, lithium batteries based on lithium metal anode, because real lithium batteries because of the risk is bigger, so rarely used daily life products. The positive material of the lithium battery is manganese dioxide or azuride, and the negative is lithium. It's easy to form lithium crystals in the cycle of charging and discharge, causing a short-circuit in the battery, and the battery is charged when the battery is finished and the battery is charged. Such a battery can also be charged, but the cycle performance is not good, and the early lithium battery is generally not charged.
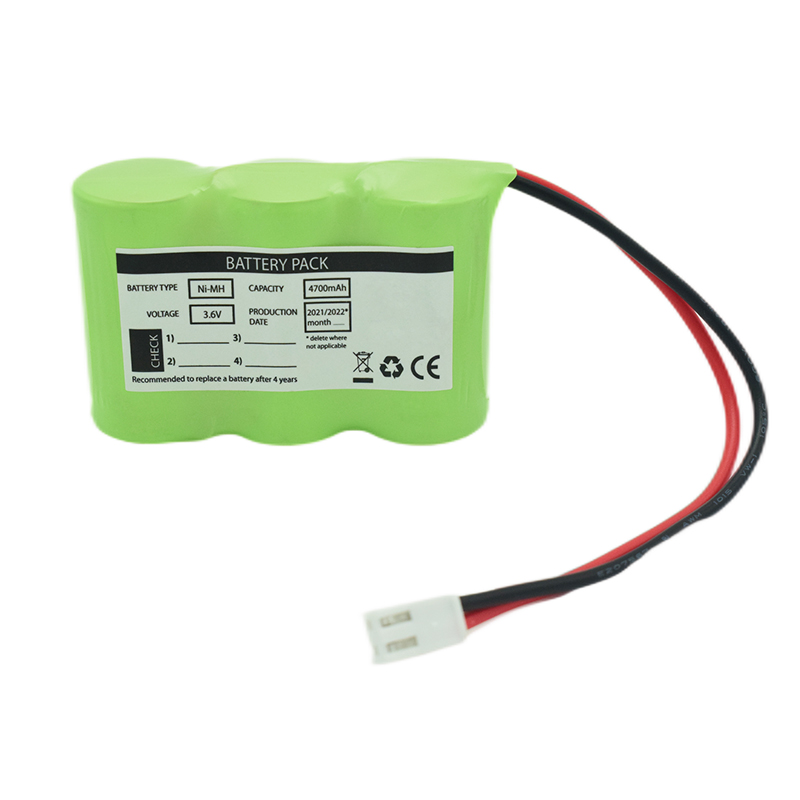

 Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V
Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V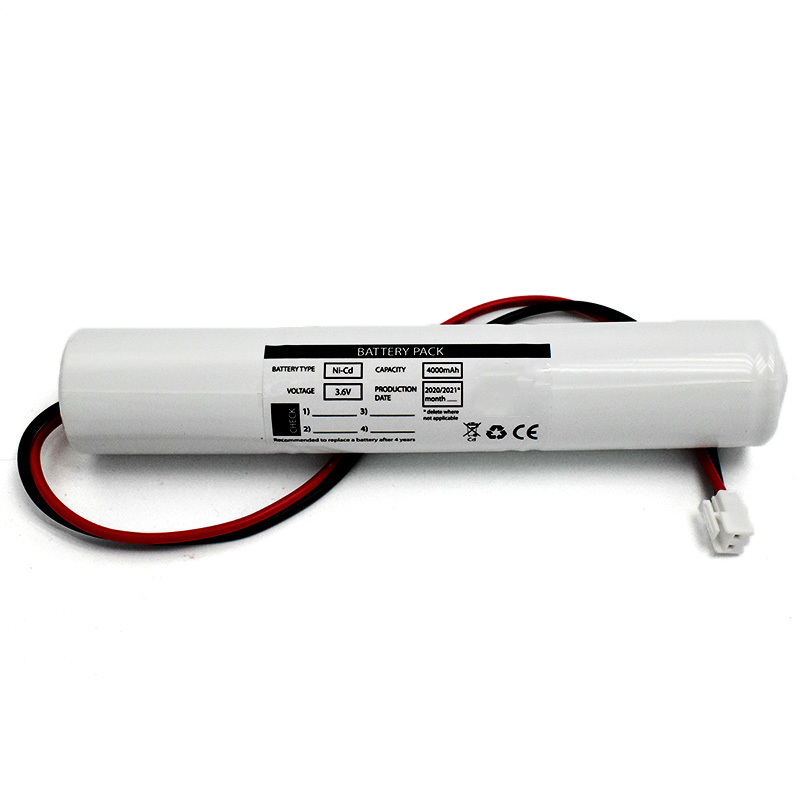 Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V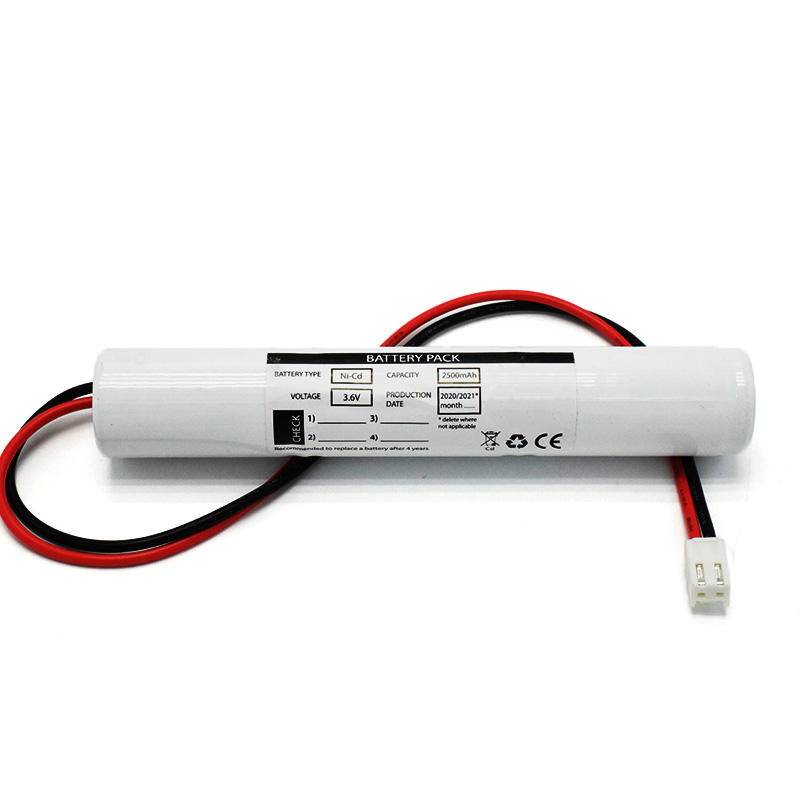 Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V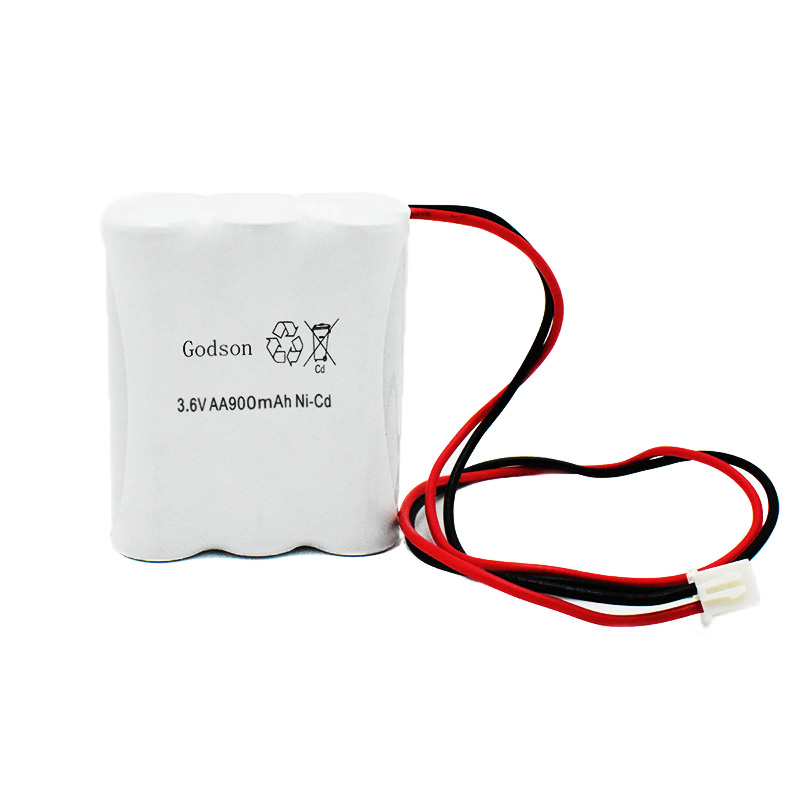 NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V
NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V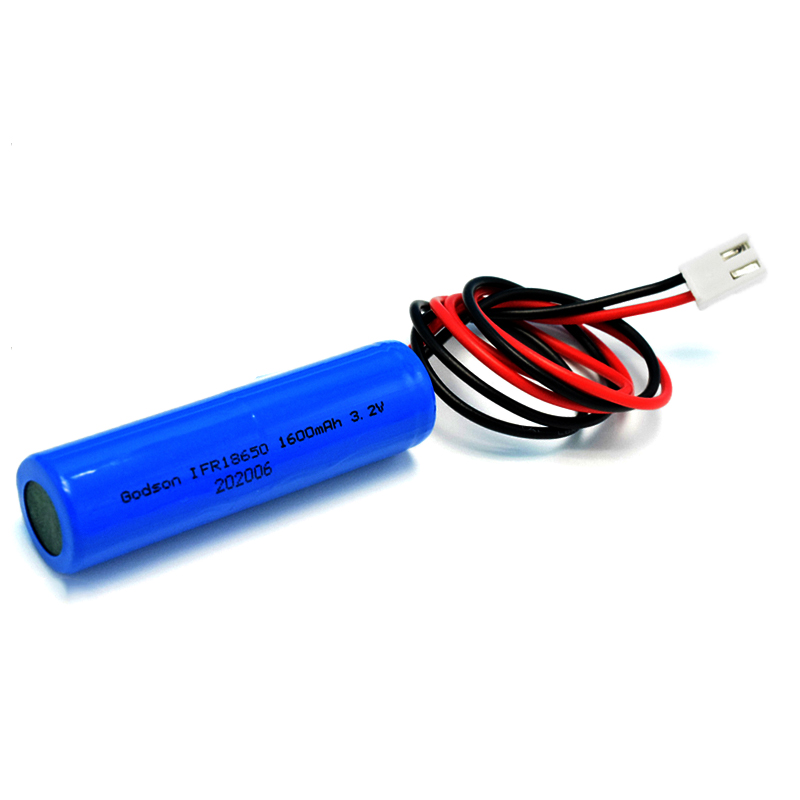 LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V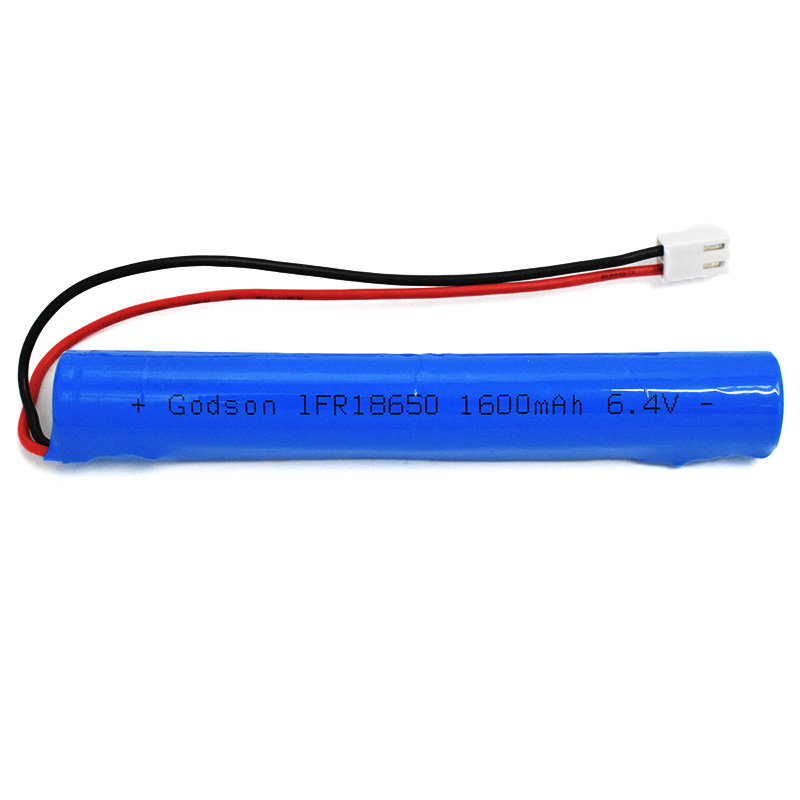 LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V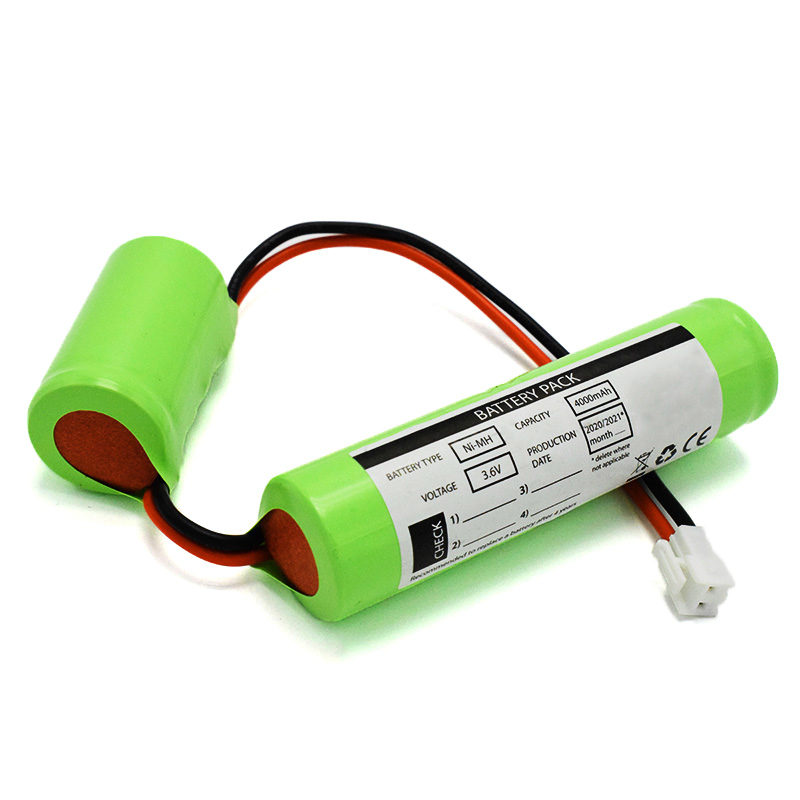 Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V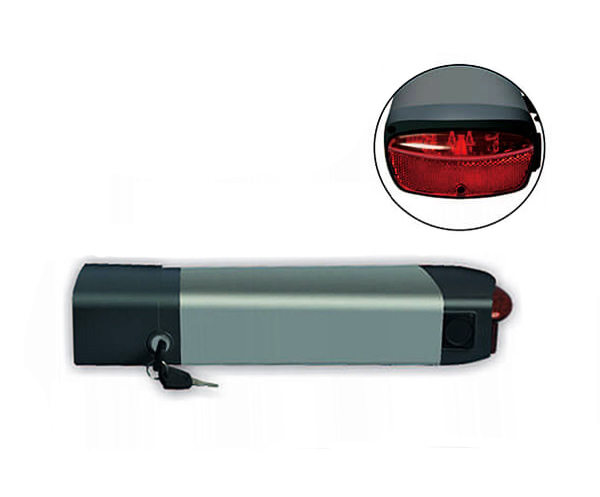 E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1
E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1 E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian
E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian