Nickel metal hydride battery is an alkaline battery whose positive active material is mainly made of nickel and whose negative active material is mainly made of hydrogen storage alloy. There has been a dramatic increase in the number of portable battery-powered electronic devices today. Some people may be confused about which batteries to purchase for these devices. This article will help consumers understand rechargeable NiMH batteries, how they work, and the benefits they provide.
Many battery applications benefit from the use of NiMH rechargeable batteries. In general, high-energy devices that are used frequently are matched with the performance characteristics of NiMH batteries. Digital cameras, GPS units and MP3 players are examples of such devices. Read everything below to learn more about NiMH batteries.
Yes, nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries are rechargeable. NiMH batteries can be recharged hundreds of times, potentially allowing them to be equivalent to hundreds of alkaline batteries in total service over their lifetime. Older generation and batteries with other chemical make-up were subject to a memory effect, which is when a battery must be fully drained before recharge or their capacity is reduced.
Do not fully discharge your NiMH batteries under any circumstances to significantly extend their life. Even if you use multiple sets during a day of shooting, if you can leave the last 10% or so in the battery, you will have a much longer life. Likewise, if you don't charge them all the way to capacity, you'll extend their life.
Modern NiMH batteries do not have the memory effect you will notice. If you carefully discharge them to the same point multiple times, you may see a minimal reduction in usable capacity. However, when you release them to another point and then recharge them, this will be removed. This is not a problem to worry about.
Nickel metal hydride has a higher energy density and performs well in terms of shelf life. Another advantage of NiMH batteries is that they are not subject to the dreaded "memory effect". NiMH batteries have a typical cycle life of 500 cycles or more.
NiMH batteries consist of two metal strips showing the negative and positive terminals and an insulating foil spacer fixed between them. This tasty energy sandwich is rolled up and placed in the battery tank with the electrolyte. The positive electrode is made especially of nickel and the negative electrode is made of metal hydride, hence the name "NiMH" or "nickel-metal hydride".
When you plug a dead battery into the charger, the current reverses the discharge process. Electrons are drawn from the positive electrode, which oxidizes and releases hydrogen gas. At the same time, the electrons return to the negative electrode, which absorbs the hydrogen. In the case of extreme overcharging, any excess hydrogen gas will be expelled from the top of the battery - look closely at the cover of the rechargeable battery to see the vent hole.
NiMH batteries don't last forever and they will eventually stop working due to wear and tear. Thank them for helping you save money, recycle them and move on.
You don't have to take your chances with the best charger on the market, but make sure it's a "smart" charger, one that electronically monitors the charging process and prevents overcharging. Not only is it better for the battery, but it consumes less power than cheap chargers, which often rely on a simple timer mechanism.
Unnecessary charging time means using more "trickle" power to hold the charge, which leads to more wear and tear and waste management. In addition, heat begins to build up in the battery, further damaging the electrolyte compounds contained therein.
Despite all advice to the contrary, fully discharging them will shorten their life and thus prolong their usefulness.
Overheating will undoubtedly damage your batteries and cause them to lose their charge more quickly.
Yes, nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries can leak, but they are generally considered safe. Leakage can occur if the battery is damaged or used incorrectly.
Why NiMH batteries leak
Damaged casing: If the battery's outer tube or label is scratched or damaged, the battery is exposed to the risk of a short circuit and leakage.
Electrolyte: The electrolyte in NiMH batteries is corrosive and can leak out if the battery is damaged.
Incorrect use: Using a battery incorrectly can cause it to leak.
If you want to know more information NiMH batteries, please contact us.We will provide professional answers.
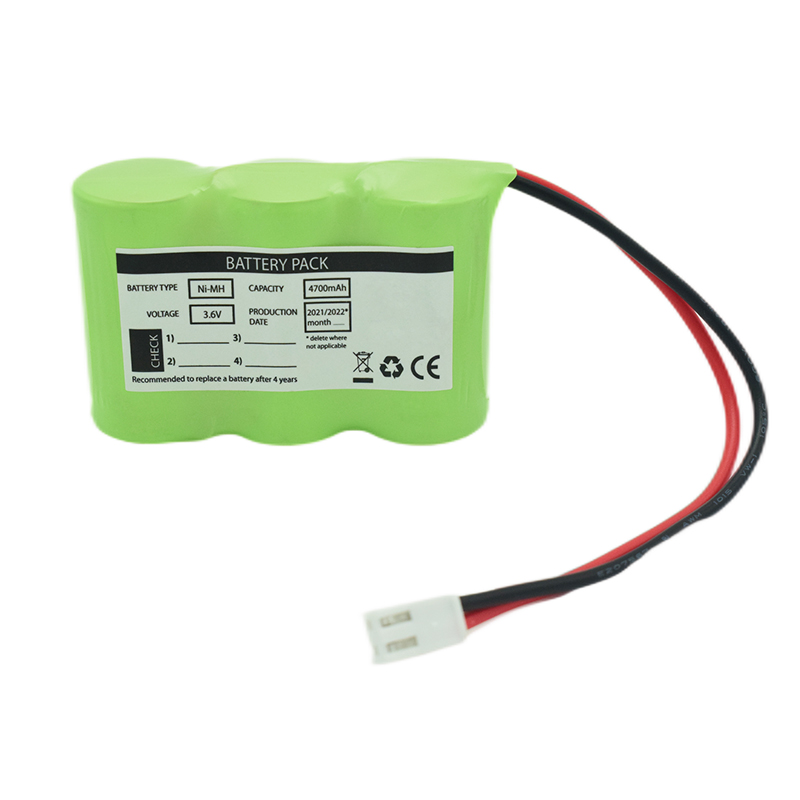
 Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V
Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V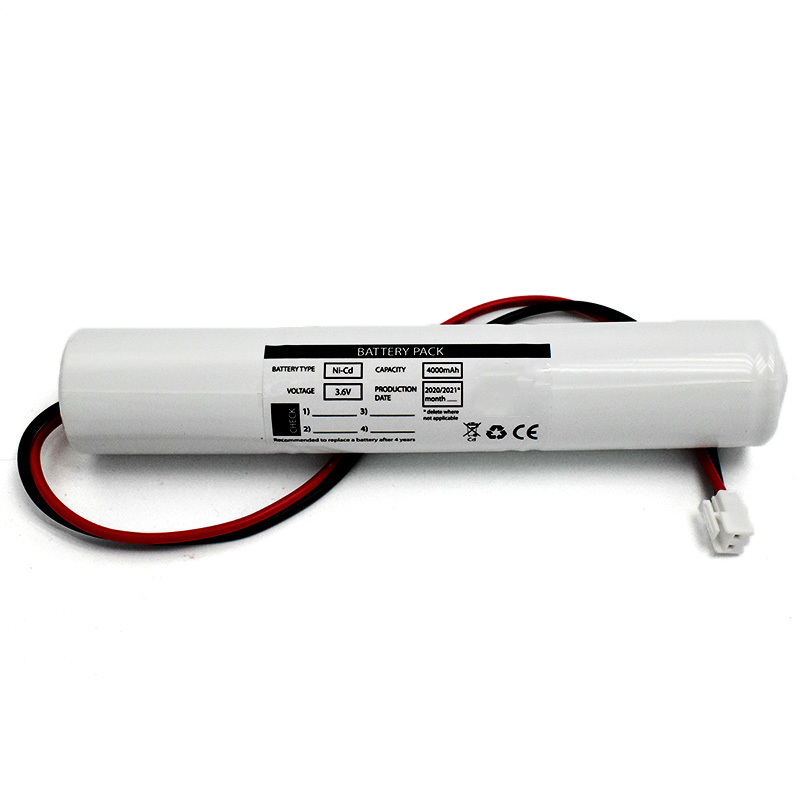 Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V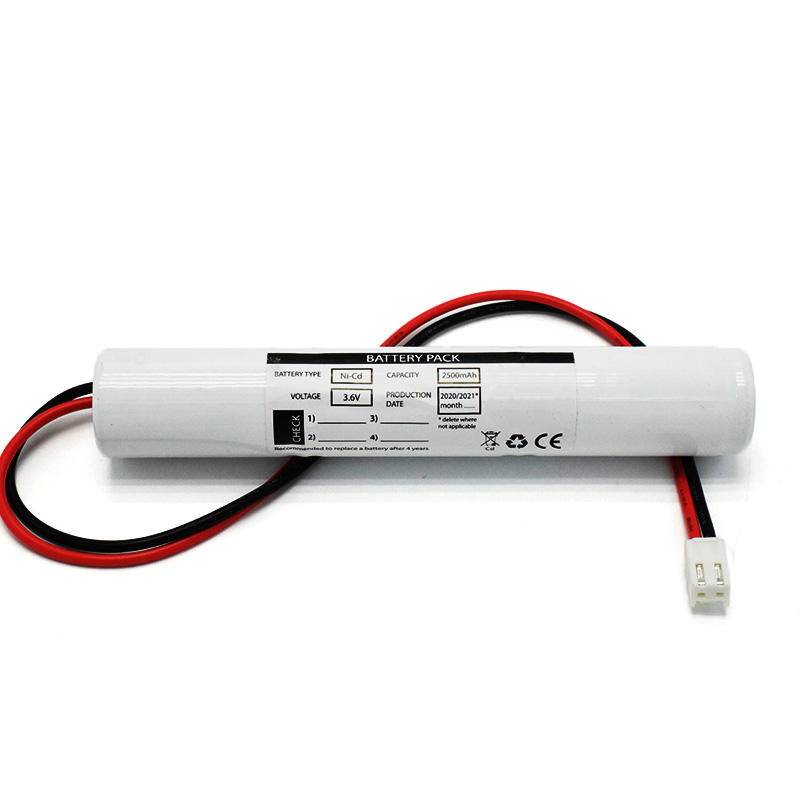 Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V
NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1
E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1 E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian
E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian