What is a battery pack?
When designing a battery pack, there are a few things to consider. Battery type, capacity, voltage, and size are all important factors.
Battery packs come in all shapes and sizes, but most contain one or more batteries of the same or similar type. The capacity of a battery pack is the total energy that can be stored in the batteries it contains. The voltage of a battery pack is the total electrical potential energy that can be generated by the batteries it contains.
The size of a battery pack is usually determined by the type and number of batteries it contains.
18650, 21700, 26650, 32700, and square batteries are the most common types of batteries used in battery packs. The number of batteries in a battery pack also determines its size;

Battery Pack Applications
Battery packs mainly provide power for electronic devices. The most common types of battery packs are lithium-ion battery packs and nickel-metal hydride batteries.
Nickel-metal hydride batteries are mainly used in consumer electronics such as children's remote control toys and cameras.
Lithium-ion batteries are used in laptops, mobile phones, and other portable electronic devices.
In addition, lithium batteries are also commonly used in robots, cars, electric forklifts, ships, and other devices that require stable power output.
Other types of battery packs include alkaline battery packs and lead-acid battery packs. Alkaline battery packs are used in some digital cameras and camcorders. Lead-acid battery packs are used in some car alarm systems and backup power supplies.
Custom Battery Pack Orientation:
Configuration Options: Users can specify the desired battery configuration, including series and parallel connections, to achieve the voltage, cell capacity, and current handling capability required for their application.
Battery Pack Sizing: The battery pack design tool helps determine the physical size and shape of the battery pack based on the selected cells and configuration. This is important to ensure that the battery pack fits the available space in the device.
Weight and Cost Estimation: Battery specifications such as capacity, voltage, chemistry, and size.
Performance Optimization: Helps optimize the performance of the battery pack and extend the battery cycle life by suggesting the best charging and discharging strategies and other parameters such as cut-off voltage.
Export Specifications: Users will be able to export battery pack design specifications including cell selection, configuration, wiring diagram, and BMS selection to facilitate the production and assembly process.
Electrical Simulation: Our design tool will provide simulation capabilities that allow users to evaluate the estimated electrical performance of the battery pack, including voltage, current, calculated internal resistance, and power output. This helps optimize the design for efficiency and safety.
Safety Considerations: This tool will provide guidelines and recommendations to ensure that the battery pack design meets lithium battery safety standards and requirements. It may also help implement features such as thermal cutouts, overcharge protection, and short circuit protection.
How to Design a Battery Pack?
During the battery pack design process. You will explore the different factors that need to be considered, from the type of battery cells to the size and shape of the battery pack.
Most battery packs also come with connectors that allow them to power electronic devices such as mobile phones, electric cars, and floor cleaners. The type of connector depends on the intended use of the battery pack;
12V battery packs are often used to power appliances in RVs, while 48V battery packs power electric forklifts.
When designing a battery pack, engineers must consider many factors, including the type of battery cells, required capacity, voltage, size, cost, safety requirements, usage environment, and more. The first step is to determine which type of battery is best suited to the needs of the device.
For example, lithium-ion batteries are often used in devices that require a steady source of power because they have a high energy density and can be recharged multiple times. Once the battery type is selected, the next step is to determine the required capacity in watt-hours (Wh). This is usually determined by the power requirements of the device and how long it needs to run on a full charge.
Once the capacity is determined, engineers must select the appropriate voltage for the battery pack. This in turn depends on the needs of the device being powered.
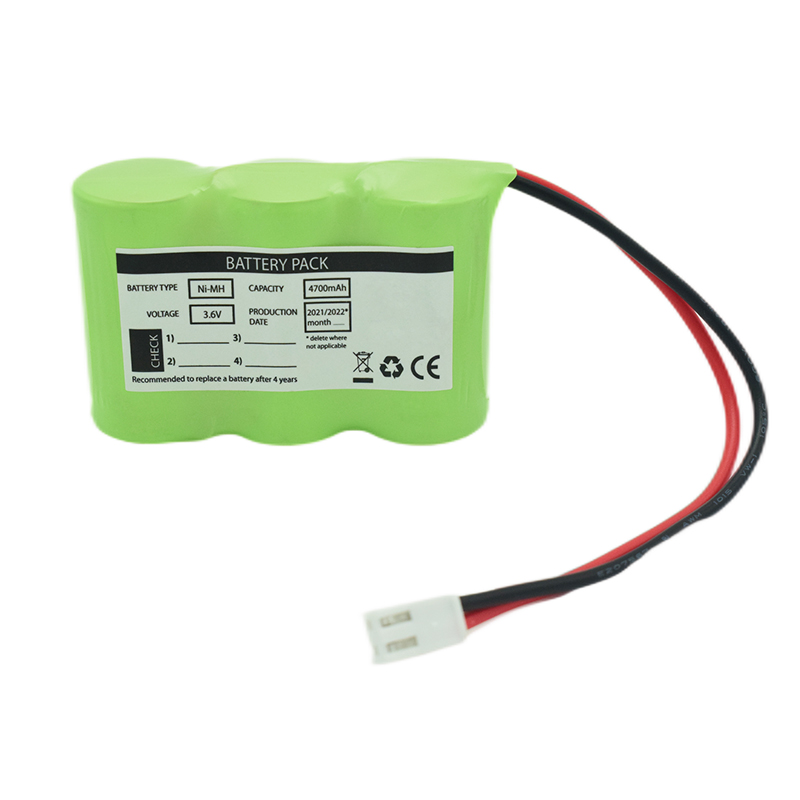
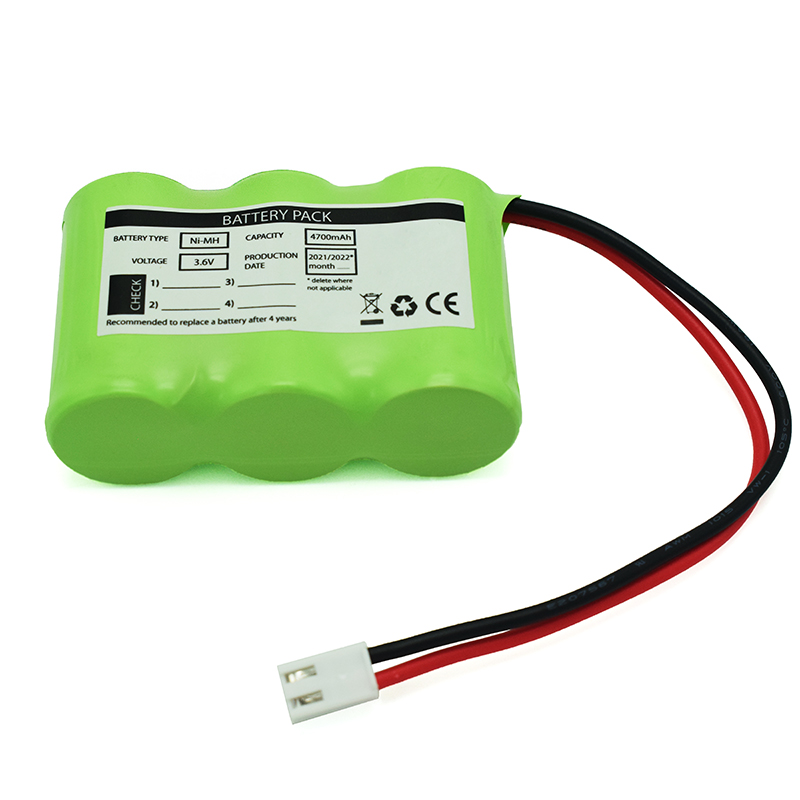
 Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V
Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V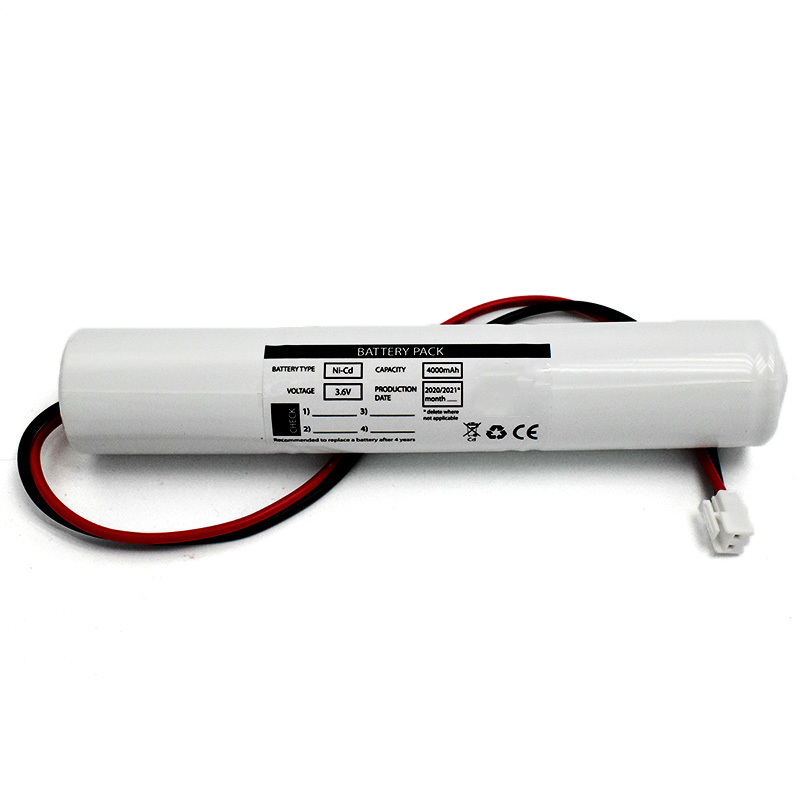 Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V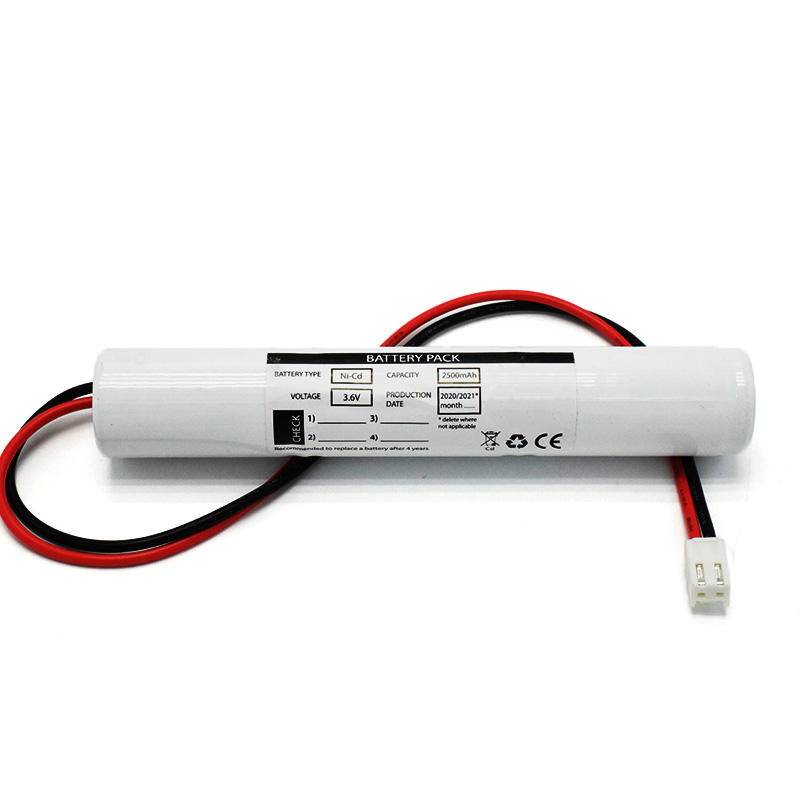 Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V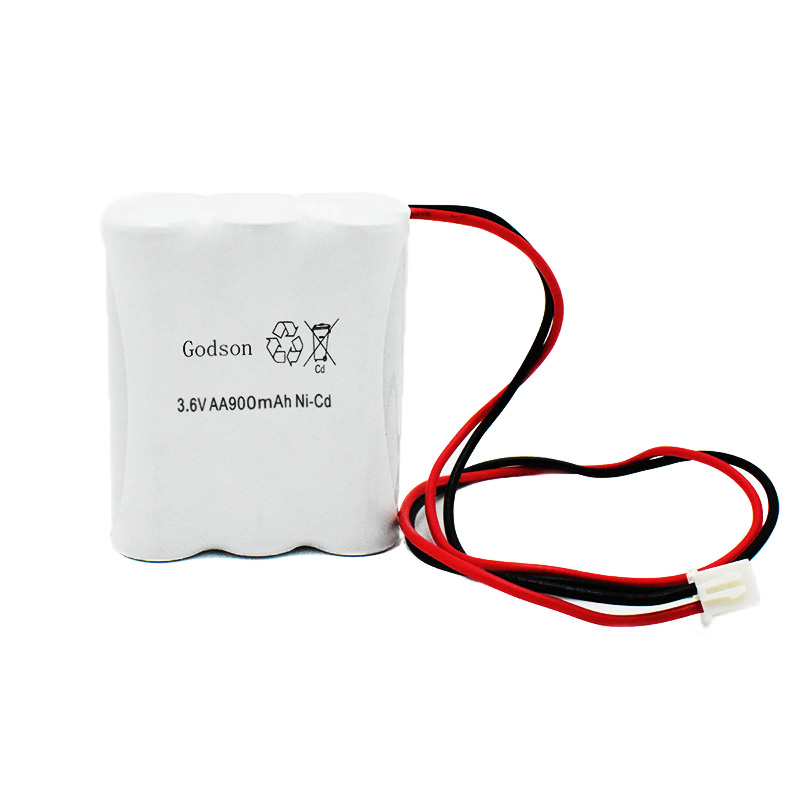 NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V
NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V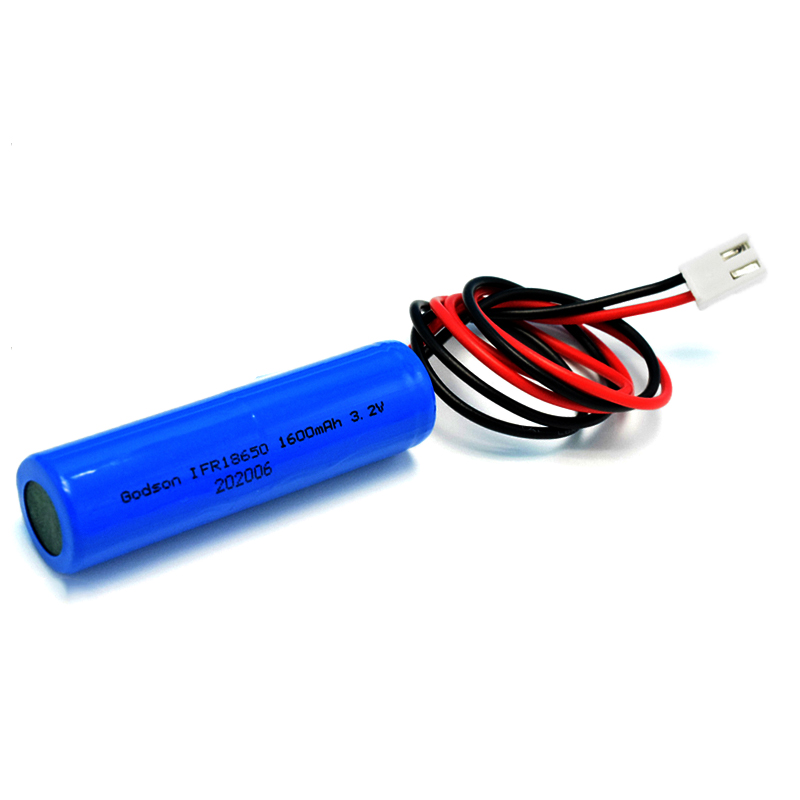 LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V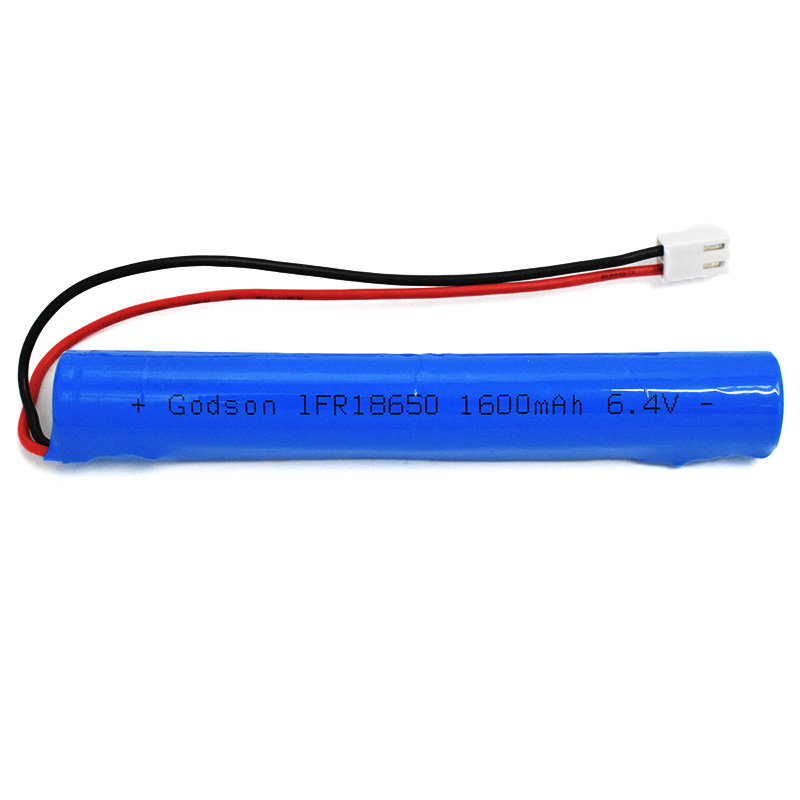 LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V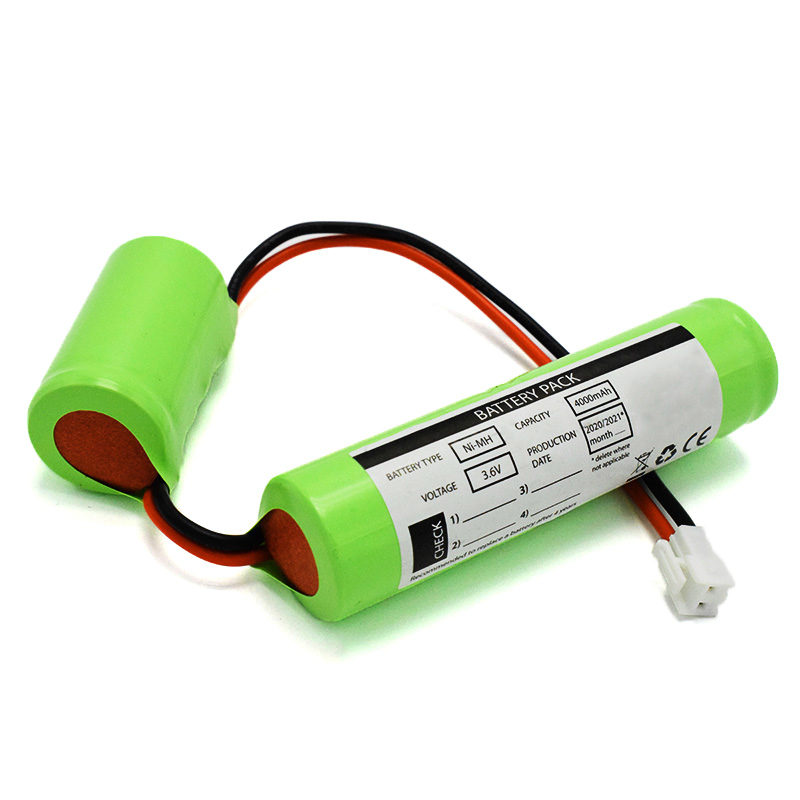 Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V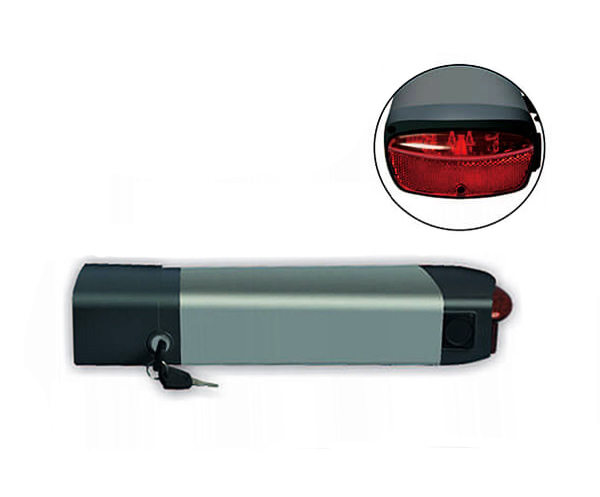 E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1
E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1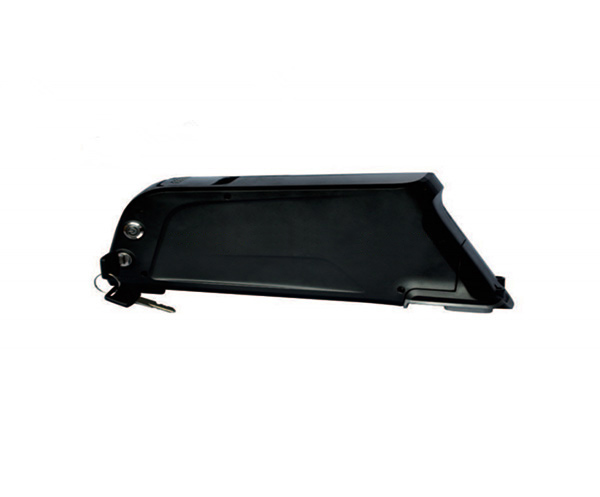 E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian
E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian