How do I charge a LiFePO4 battery? This is one of the most common questions we get from our customers. The answer is simple: use a LiFePO4 battery charger, of course. When charging LiFePO4 batteries, make sure you are not using a charger for other lithium-ion chemicals that are typically designed for higher voltages than what is required for LiFePO4. We are often asked if we can use a lead-acid battery charger to charge LiFePO4. The short answer is yes, as long as the voltage is set within the parameters acceptable for LiFePO4 batteries.
LiFePO4 batteries do not need to be recharged after each use if they are not fully discharged. liFePO4 batteries are not damaged when they are in the partially charged state (PSOC). You can charge the LiFePO4 battery after each use or after it has been discharged to 80% DOD (20% SOC). If the Battery Management System BMS) disconnects the battery due to low voltage (voltage will be <10V), use the LiFePO4 battery charger to remove the load and recharge immediately.
LiFePO4 batteries can be safely charged between 0°C and 45°C (32°F and 113°F). LiFePO4 batteries do not require temperature compensation for voltage when charging in high or low temperature conditions. If the BMS is disconnected due to low temperatures, the cell must warm up to allow the BMS to reconnect and receive charging current. If the BMS is disconnected due to high temperature, the battery needs to cool before the BMS can accept the battery charge. For BMS low and high temperature disconnect and reconnect values, refer to the data sheet for the specific battery.
Most lead-acid battery chargers can be used with LiFePO4 batteries as long as they fall within the appropriate voltage guidelines. Liquid-rich battery charging algorithms typically have voltages higher than the LiFePO4 charging requirement, which will cause the BMS to disconnect. If this happens, it is often good practice to replace the charger with a LiFePO4 charging profile. Since the BMS protects the battery, using a lead-acid charger will not normally damage the battery.
Note that if the BMS is disconnected due to low voltage, the lead-acid battery charger may not be able to reconnect the BMS, even if the charger has acceptable charging parameters to charge LiFePO4. This is because when the BMS is disconnected, the LiFePO4 battery has no voltage and the voltmeter reads 0V, while the lead-acid charger needs the battery to read voltage to start charging. If the battery reads 0V, the lead acid battery charger will not recognize that the battery is connected and should start charging. This is also true for some low quality Li-ion battery chargers. It is always recommended that you invest in a high quality LiFePO4 charger to ensure high performance and longevity.
When connecting LiFePO4 cells in parallel, make sure that the voltage between each cell is within 0.1V of each other before putting them into use, this will minimize the chance of imbalance between cells. If you are charging 12V LiFePO4 cells, the charging voltage should be between 14V - 14.2V. When charging 24V cells in parallel, the charging voltage should be 28V - 28.4V. Charging 36V LiFePO4 cells in parallel requires a voltage of 42V - 42.6V. Finally, charging a 48V LiFePO4 battery requires a voltage parameter of 56V - 56.8V. The table below summarizes the voltage requirements for each system voltage.
The voltage parameters apply to the charging curves CC and CC-CV. If your charger voltage is lower than the voltages listed in the table, it will not damage your battery, but it will undercharge and will not provide the full rated capacity of the battery. If your charger voltage is higher than the voltages listed in the table above, the BMS may disconnect the battery and you may need to remove the load to reconnect it. We recommend that you replace your charger to avoid this inconvenience and invest in a high quality LiFePO4 battery charger.
When connecting cells in series, make sure that the voltage between each cell is within 50mV (0.05V) before putting them into use. This will minimize the possibility of imbalance between cells. If your cells are out of balance and the voltage of any cell is greater than 50mV (0.05V) from another cell in the group, you should charge each cell individually to rebalance. You can periodically charge each cell individually to avoid imbalance. When charging LiFePO4 cells in series, it is best to use multiple chargers to charge each cell individually to ensure that the cells remain balanced. If you want to charge the entire system, you can also use a 24V battery LiFePO4 charger or a 48V battery LiFePO4 charger.
Depending on the quality of the alternator, the LiFePO4 battery can be charged without modification. However, a low-quality alternator with poor voltage regulation can cause the BMS to disconnect the LiFePO4 battery. If the BMS disconnects the battery, the alternator may be damaged. To protect your LiFePO4 battery and alternator, be sure to use a compatible, high-quality alternator or install a voltage regulator. You can also use DC to DC chargers to safely and efficiently charge your batteries, including home banks. When using an alternator to charge LiFePO4 batteries, it is recommended that a DC to DC charger be installed.
If you are using a voltage-based fuel gauge that is designed for lead-acid batteries, it will not accurately measure the state of charge (SOC) of LiFePO4 batteries. Please replace your fuel gauge with one that measures current rather than voltage to accurately measure the state of charge of lithium iron phosphate batteries.
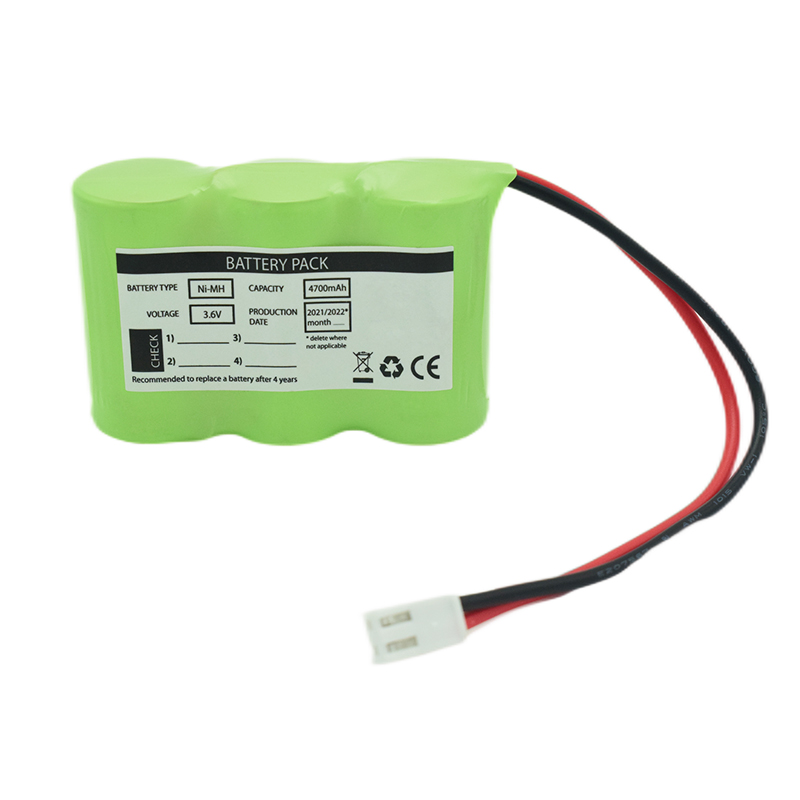
 Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V
Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V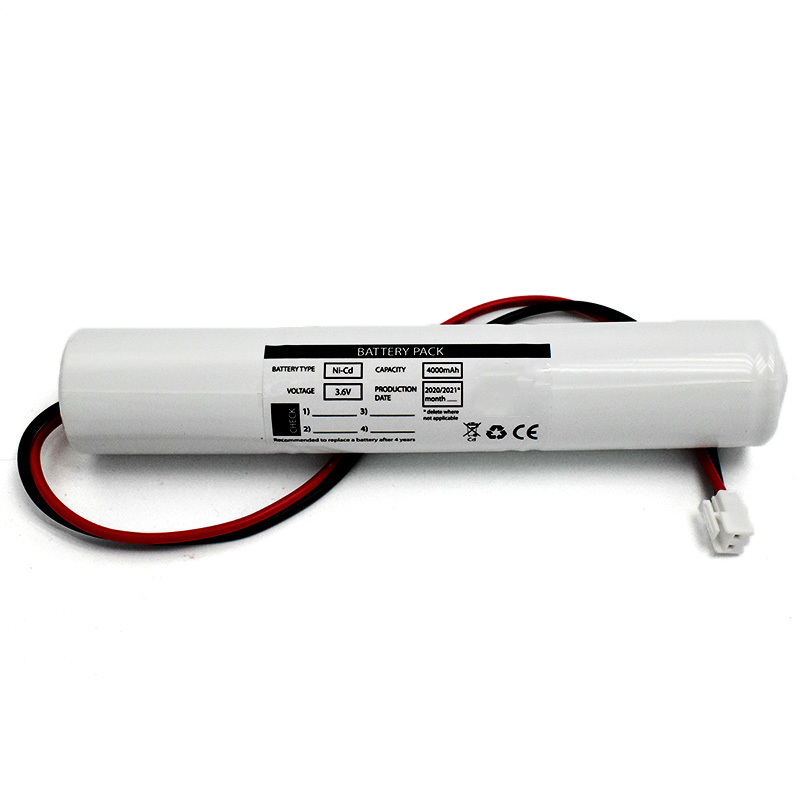 Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V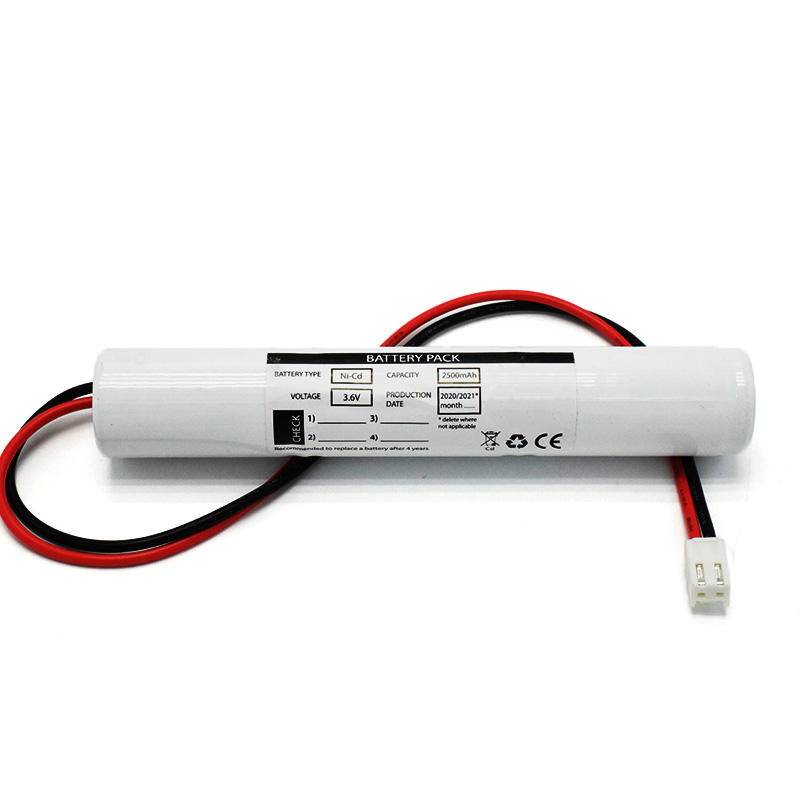 Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V
NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1
E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1 E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian
E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian